Restful API Architecture
Need for it:
- With the increasing complexity of web applications and the proliferation of devices and platforms, there arose a need for a standardized, scalable, and flexible approach to designing web APIs.
- Traditional web services often lacked uniformity and were cumbersome to use and maintain. RESTful API architecture addressed these challenges by providing a standardized set of principles and practices for building APIs.
What is it:
- RESTful (Representational State Transfer) API architecture is an architectural style for designing networked applications, particularly web services.
- It is based on a set of principles and constraints that emphasize a client-server model, statelessness, uniform interfaces, and scalability.
- RESTful APIs use HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) to perform operations on resources, and they represent these resources using URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers).
Architecture:
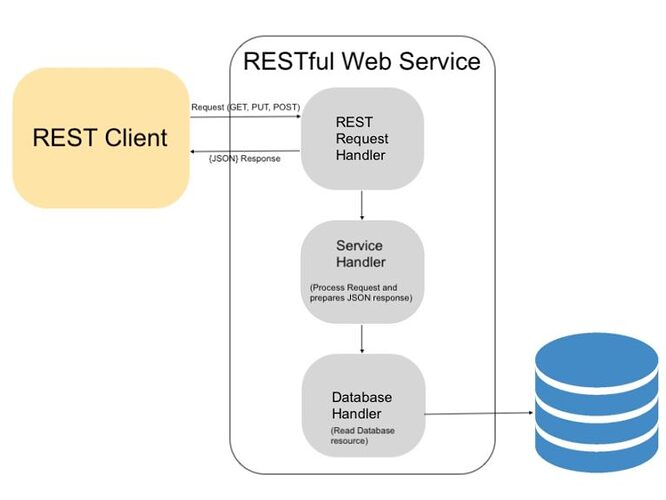 REST_architecture768×576 26 KB
REST_architecture768×576 26 KB
How is it used in the real world:
- RESTful API architecture is widely used in the real world for building APIs that power a variety of web and mobile applications.
- It provides a simple, lightweight, and standardized approach to exposing data and functionality over the web.
- Companies and organizations across various industries leverage RESTful APIs for a multitude of purposes, including:
- Providing data and services to front-end web and mobile applications.
- Enabling integration between different systems and applications.
- Exposing functionality for third-party developers to build upon (e.g., through API platforms).
- Supporting microservices architecture, where each microservice exposes a RESTful API for communication with other services.
- RESTful APIs have become the backbone of modern web development, facilitating interoperability, scalability, and ease of integration across diverse systems and platforms.